Organic solar cells hold significant promise due to their lightweight nature, flexibility, and ability to be processed via solutions. These attributes make them highly applicable in areas such as wearable electronics, photovoltaic building integration, and photovoltaic agriculture. However, they face substantial challenges, including a high exciton binding energy and weak driving forces, which hinder the efficient dissociation of excitons and result in lower current outputs compared to inorganic systems with similar band gaps. Additionally, the photothermal process can cause severe self-aggregation within the photosensitive layer, leading to excessive phase separation and an inability to form an ideal interpenetrating network structure. This exacerbates issues related to exciton dissociation and charge transport, ultimately compromising the photothermal stability of organic photovoltaics. Consequently, boosting exciton dissociation efficiency and photothermal stability remains a critical hurdle in advancing organic solar cell technology.
In addressing these challenges, Xichang Bao from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Process at the Chinese Academy of Sciences made notable strides based on prior research (Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003654). By leveraging the differing solubilities of polyarylether and photovoltaic acceptor materials and employing a layer-by-layer coating technique, his team successfully fabricated planar heterojunction organic solar cells. This approach not only enhances molecular packing within the photosensitive layer but also boosts charge recombination and extraction capabilities, achieving a remarkable photoelectric conversion efficiency of 18.6%. Furthermore, the insulating resin embedded within the photosensitive layer forms a matrix network structure that mitigates material self-aggregation, thereby improving the device's photothermal stability. These findings were reported in ACS Energy Letters. Further investigation revealed that polyarylether materials are evenly dispersed throughout the photosensitive layer, inspiring the concept of organic photovoltaic "pins." This innovation increases the dielectric constant and built-in electric field of the organic photosensitive layer, enhancing carrier transmission and collection efficiency. The results were published in Nano Energy. This body of work unveils a novel mechanism by which insulated polyarylether resin materials enhance the performance, photothermal stability, and flexible tensile properties of organic solar cells, offering fresh perspectives for the creation of efficient and stable organic photovoltaics.
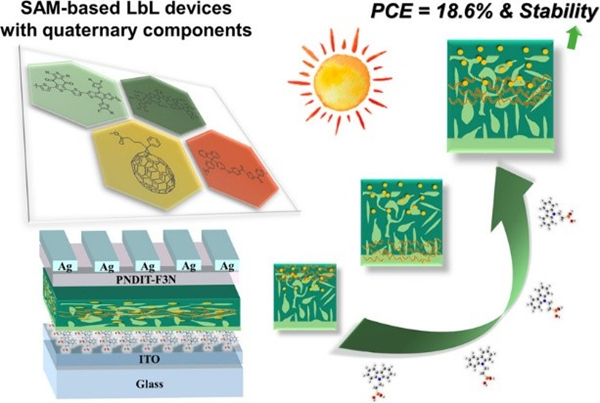
This advancement represents a significant leap forward in overcoming long-standing limitations in organic solar cell technology, setting the stage for future innovations in renewable energy solutions.
Wood Veneer,charcoal panel ,3d wood veneer sheet,wood veneer panels
Linyi Dongtai Decoration Materials Co., Ltd , https://www.dongtaiwood.com