Foreword: In 2018, the global PV installation volume is about 103.3GW, China continues to lead with 44.26GW, followed by the US 11.36GW, the top 5 is India 9.3GW, Japan 6.2GW, Australia 3.8GW. The number of countries entering the GW-class market has increased to 15. The overseas market is becoming a new corner for Chinese PV companies. Understanding and deepening the overseas market and formulating product strategies and market strategies suitable for overseas markets are the key to gaining market share. Different countries have different power grid structures, photovoltaic standards, photovoltaic policies, and market environments, which brings complexity and difficulty for Chinese PV companies to explore overseas markets. This article describes the Indian PV market.
1. Development and current status of the Indian PV market
India is the most competitive country and region in the world. The country's politics is relatively stable, its economic growth prospects are good, its population structure is excellent, and its geographical position is superior.
India is a country with extremely uneven power supply and demand. In the past 10 years, power supply has been insufficient, and the power supply and demand situation is more severe. According to estimates by relevant departments, India's power gap in 2015 peaked at 2.6%. By 2022, the Indian power gap may increase to 5.6%. At present, about 300 million people in India's nearly 1.3 billion people are unable to use electricity normally, accounting for about 23% of their total population.
In January 2014, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the solar energy revitalization plan: by 2022, India will achieve a total of 175 GW of renewable energy, including 100 GW of solar installed capacity (40 GW solar roof power generation project and 60 GW medium and large projects). Solar grid-connected projects), with a total investment of about 8,000 to 100 billion yuan.
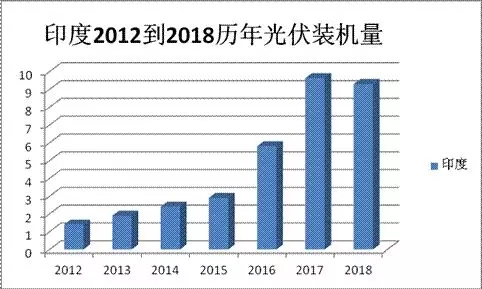
In 2012, India's PV installations were 1.4GW, compared with 1.9GW in 2013. In 2017, it reached an all-time high of 9.73GW, and in 2018 it dropped slightly to 9GW. It is estimated that India's renewable energy installed capacity will increase by 15.86GW in 2019. At present, India is already the fifth largest installed PV market in the world and the second largest installed market.
Nearly 90% of solar panels and inverters in the Indian market come from imports, most of which are from China.
2. Introduction to solar energy resources in India
India has great potential for developing solar energy. Its lighting conditions are significantly better than China's. It is located in tropical and subtropical regions. Due to its proximity to the equator, most of the country has about 300 sunny days all year round, with sufficient sunshine hours and annual solar radiation of up to 1700-2500kWh. /kWp, the daily average solar radiation can reach 4.0-7.0kWh/m2, and solar radiation resources are among the best in the world's major economies, better than China, the United States, Japan and the European Union.
3. India's power grid, electricity price, and photovoltaic standards
The Indian grid voltage is the same as that in mainland China. The low voltage is single-phase 230V and three-phase 400V, and the frequency is 50Hz.
In 2017, India’s ordinary lending rate was 9.51%. Although it is lower than 2016, it is still at a relatively high level. This means that if India’s PV power plants are financed from domestic banks in India, the actual financing costs will be greater than 10%, higher financing costs have increased the electricity cost of photovoltaic power generation in India to a certain extent.
According to data surveys, the weighted cost per kW of photovoltaics in India in 2017 was US$971, even lower than the system cost in China. The world's leading lighting time and low cost cost made India achieve even higher interest rates. Low electricity costs. Solar projects account for nearly 40% of India's new energy generation. Solar power prices in India have also fallen, hitting a record low, and solar energy is already cheaper than coal.
On June 30, 2008, India issued the National Climate Change Action Plan, and in November 2009, the National Solar Energy Plan was implemented. On August 30, 2017, the BIS Mandatory Registration Act for Photovoltaic Products in India, the Quality Control Act for Solar Photovoltaic Systems, Equipment and Components, was issued by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE). It was promulgated on September 7. From September 5, 2018, all solar PV systems, equipment and components sold in the Indian market must pass BIS CRS certification.
India adopts international common standards. For example, inverters adopt IEC62116, IEC61727, EN62109-1/-2, etc., PV products enter the Indian market, and must pass the environmental and efficiency test in India. The environmental test adopts the IEC60068 standard, and the efficiency test is adopted. IEC61683 standard.
4. India's PV policy
In the history of India, there have been anti-dumping investigations on photovoltaic products exported to India from China and other countries. The PV trade policy has been repeated many times. On November 23, 2012, the Indian Anti-Dumping Authority announced its application under the Indian Solar Manufacturers Association. Decided to conduct anti-dumping investigations on solar cells from mainland China, Chinese Taipei, Malaysia and the United States. On May 22, 2014, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry of India issued a final ruling on the case and proposed an anti-dumping duty of US$0.11 to US$0.81 per watt. In the end, the Indian Ministry of Finance chose not to implement the Indian Ministry of Commerce and Industry's ruling, and closed the case without tax. In July 2017, the Anti-Dumping Bureau of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry of India issued an announcement stating that it should initiate an anti-dumping investigation on photovoltaic cells and components imported from China, Taiwan and Malaysia in response to its domestic industry application. In March of this year, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry of India issued an announcement to decide to terminate the above anti-dumping investigation.
In December 2017, the Indian Ministry of Finance issued an announcement to initiate a safeguards investigation into solar photovoltaic products (including crystalline silicon cells and components and thin-film batteries and components) entering India based on the application of the Indian Photovoltaic Manufacturers Association. On January 5, 2018, the Indian side made the preliminary ruling of the case. The General Directorate of Safeguards of India proposed a temporary measure to the Central Government of India, which imposed a 70% ad valorem tax on solar photovoltaic products entering India as a temporary safeguard measure. 200 days. Affected by this policy, China's components and battery chips exported to India in the first half of 2018 were only about 3.6 GW and 0.7 GW, a decrease of about 33% compared with the same period in 2017.
India approved the second phase of the 4022 grid-connected rooftop solar project in 2022. The central government will provide a subsidy of 181 billion rupees (about 1.656 billion US dollars) to support household solar systems and incentive distribution companies. The household solar system with a installed capacity of 3kW provides 40% subsidy support and 20% subsidy support for 3-10kW rooftop PV systems. The roof system of the Collective Housing Association or the Residential Welfare Association will receive an additional 20% subsidy. In this case, India's support for each household's solar system is limited to 10 kW, and the support for the GHS/Residential Welfare Association is limited to 500 kW per project. The above subsidy support will be extended to 4 GW of household installed capacity items and will be provided to individual systems based on the baseline cost or bidding cost, whichever is lower.
The Indian government is extremely optimistic about the launch of this plan. According to the plan, the government expects to add up to 38 GW of rooftop PV projects and create 939,000 jobs in 2022.
5. Indian market risk
In May 2018, the Indian Solar Energy Corporation (SECI) issued a joint bid for 10 GW of photovoltaic manufacturing, which attracted enthusiastic attention from the industry. Surprisingly, the large-scale 10 GW PV manufacturing joint bidding was repeatedly postponed six times and eventually attracted only one bidder. So far, SECI data shows that the 2.4GW PV bidding in the second phase of 3GW solar tendering was cancelled, and the 1.3GW solar tender in the 2.5GW landscape joint tender and the third part of the 3GW solar tender were also cancelled.
1) Excessive government intervention: Statistics show that 85% of India's solar products currently rely on imports from China and Malaysia. The Indian government has been working hard to support India's own photovoltaic manufacturing companies, so it has adopted a punitive taxation to curb the growing imports of photovoltaic products. A 25% guarantee tax (SGD) is imposed on China's imported solar modules. Tariffs are transmitted to investors through yields, forcing the cost of building power stations to increase, eventually leading investors to abandon bids announced by government agencies.
2) Bidding and auction methods are not standardized: The government proposes a bidding concept linked to the manufacturing industry. Investors are both developers and manufacturers, setting too high investment thresholds, and some prospective investors are rejected. Hey, no one is interested in the tender. The highest on-grid tariff set in the bidding is too low, and the company has no profit margin. India is one of the countries with the lowest average market price of photovoltaic products in the world.
3) Compared with other countries, India's PV manufacturing industry chain is incomplete, from silicon materials, silicon wafers, batteries to final components, and supporting auxiliary materials. India's local production capacity is weak, and silicon materials in the upstream of the industrial chain. There are almost no companies involved in the silicon segment. The weak production base has limited some companies to invest in India. The construction of the Indian power grid has been lagging behind for many years, and the power grid structure is weak. Delays in land approvals and land acquisition disputes in India have exacerbated the plight of solar investment.
Nylon Mesh is a chemical fiber woven mesh made by chemical processing of nylon, nylon, polyester, and nylon fibers as raw materials. Jinlun has the function of high temperature and alkali resistance, polyethylene has the effect of acid resistance, nylon mesh is the general name of these chemical fiber woven mesh. Nylon mesh includes: (nylon blend,) nylon mesh, polyvinyl chloride mesh, sunshade mesh.
Nylon nets include: (nylon blends,) nylon nets, polyethylene nets, and sunshade nets, which are widely used in plant shading, marine aquaculture, flour processing, nylon screen printing, pharmaceuticals, paint filtration, and well-drilling. It has the function of high temperature and alkali resistance, and polyethylene has the effect of acid resistance.
Nylon mesh has the characteristics of high toughness, good elasticity, corrosion resistance, oil resistance, water resistance, wear resistance, high temperature resistance, weather resistance, etc .; it also has good insulation, low lubrication coefficient and other characteristics.
Widely used in industrial filtration, petroleum, chemical, printing and other products with complete specifications, excellent quality, special specifications can be customized. And screen printing, paint filtration, fishing and other industries. Nylon mesh has the effects of high temperature resistance and alkali resistance, and polyethylene mesh has the effect of acid resistance.
Nylon Mesh
Nylon Wire Mesh,Nylon Mesh Netting,Nylon Mesh Screen,Black Nylon Netting
Jieyang Xinxin Industry and Trade Co., Ltd. , https://www.gdxxgm.com