Recently, Wuhan University of Science and Technology jointly established the State Key Laboratory of Refractory Materials and Metallurgy, and the paper "In Situ Construction of γ-MoC/VN Heterostructured Electrocatalysts with Strong Electron Coupling for Highly Efficient Hydrogen Evolution" Reaction" was published in the TOP journal "Chemical Engineering Journal" (impact factor: 10.652).
Hydrogen evolution reaction is the basic reaction for the production of hydrogen by electrolysis of water. High-efficiency and low-cost electrocatalysts are essential to reduce overpotential and improve hydrogen evolution efficiency. Transition metal carbons and nitrides such as Mo2C, MoC, Mo2N, WN, etc., have catalytic activity similar to Pt and have been extensively studied. However, bulk and pure phase transition metal carbons and nitrides lack sufficient active sites and strong The metal-hydrogen bonding inhibits their catalytic activity in the hydrogen evolution reaction. It is a very effective method to improve the water splitting and hydrogen absorption/desorption efficiency of the catalyst by constructing heterostructures and interfaces. How to design an excellent two-phase interface and electronic coupling efficiency has always been a design difficulty.
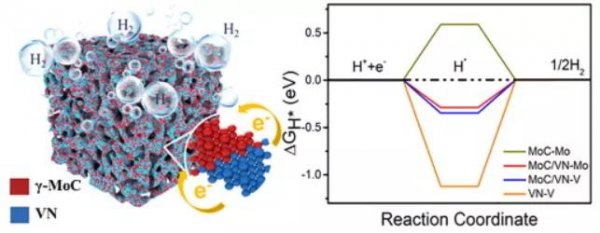
In response to the above problems, this work designed a ternary metal oxide as a precursor, and synthesized molybdenum nitride and vanadium carbide heterostructures (γ-MoC/VN) through a stepwise in-situ carbonization and nitridation method. The heterogeneous interface of molybdenum nitride and vanadium carbide leads to strong electronic coupling, promotes electronic transfer at the interface, and effectively improves the hydrogen evolution activity of the material. On the other hand, the multi-step in-situ gas phase reaction makes γ-MoC/VN rich in a large number of pore structures, exposing more active sites, and also provides a convenient channel for the diffusion of the electrolyte and the escape of H2 bubbles, so γ-MoC/VN The VN composite exhibits excellent electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution kinetic performance. The research results have important guiding significance for the design and development of high-performance electrolysis water hydrogen production catalysts.
The first unit of this thesis is the State Key Laboratory of Refractories and Metallurgy and the Institute of Advanced Materials and Nanotechnology jointly established by Wuhan University of Science and Technology. Professor Huo Kaifu and Associate Professor Zhang Xuming are the corresponding authors of the results, and PhD student Pi Chaoran is the first author.
This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Natural Science Foundation-Henan Joint Fund Key Project, the Hubei Province Natural Science Innovation Group, the Hubei Province Technological Innovation Major Project, the provincial and ministerial joint construction of the State Key Laboratory of Refractories and Metallurgy, and Supported by Wuhan University of Science and Technology Excellent Doctoral Dissertation Cultivation Project
Formic Acid has strong reducing ability and is a by-product of coking. Adding Formic ACID is more effective than adding inorganic acids such as H2SO4 and HCL, because inorganic acids have only acidification effect, and formic acid can not only reduce the pH value of silage, but also inhibit Plant respiration and poor microbial fermentation.
Formic Acid
Formic Acid In Water,Formic Acid To Oxalic Acid,Acetic Acid To Formic Acid,Formic Acid And Acetic Acid
ZIBO JUNTU INTERNATIONAL TRADE CO.,LTD , https://www.juntuchem.com